Programme d'éducation à la sécurité routières
Here are the general steps in chronological order :
-
1- Registration
You must register at the driving school of your choice and pay the initial down payment.
-
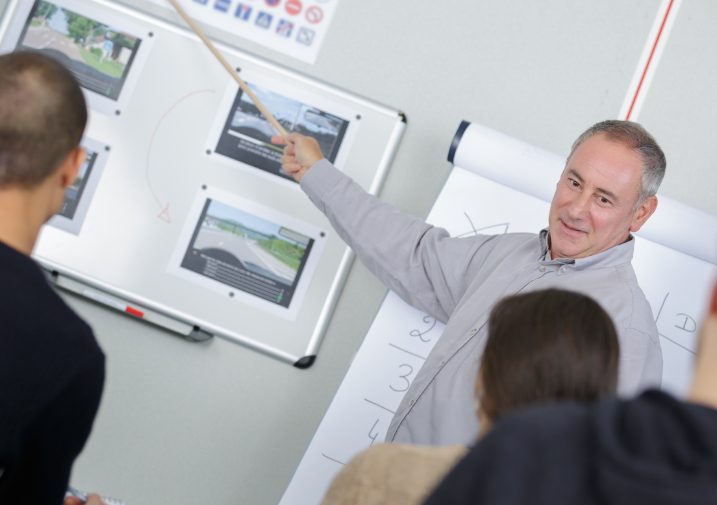
2- Theoretical examination
Following your registration, you must attend the first nine (9) hours of classroom theory and successfully pass the theory test coordinated by the driving school instructor during the tenth (10) hour of classroom theory. This must be completed within a minimum of 30 days.
-
3- Certificate
Following the correction and success of your theory exam in class, a representative of the driving school will issue you a ”Proof” certificate which will confirm that you have successfully passed your theory exam.
-
4- Present at an SAAQ office
Once you have this attestation, you can then go to an SAAQ office to get your learner’s permit back without having to take an additional theory test at that time.
N.B. You must present the following documents to the SAAQ in order to recover your learner’s permit:- Your Theory Course Certificate issued by the school following the successful completion of your in-class theory exam.
- Two pieces of identification.
- And or parental consent if you are under 18 years of age. Document provided by the SAAQ: Parental Consent
-
5- Second theory exam
Once you have your apprenticeship permit in hand, you will be asked to complete in the respective order over the following 12 months: Phase (2), Phase (3) and Phase 4 are the 14 hours of theory in class and the remaining 15 road trips.
Important : After a total of 10 months following your learner’s permit, you will be eligible to take a second theory test at the Société de l’assurance automobile du Québec. -
6- Final exam
This general theory exam will cover all the theory taught in the previous phases and the material recorded in the Route Access Booklet. Following the success of this (2) second theoretical exam executed in the SAAQ office, you will have to wait (2) additional months before being able to plan your final exam on the road.N .B. You must have successfully completed the entire theoretical program and the 15 road trips, obtain the certificate of the driving school with the successful mention, before being eligible for the final examination on the road.
Ce que vous devez savoir:
- Le nouveau programme d’éducation à la sécurité routière comprend un total de 39 heures d’enseignement.
- Les 39 heures de formation sont réparties de la façon suivant: 24 heures de théories en classe ainsi que 15 sorties sur la route.
- Le programme comprend cinq principes directeurs : l’alternance entre la théorie et la pratique, la conduite autonome, l’écoconduite, la stratégie OEA et l’information sur les comportements à risques.
Le processus total s’échelonnera donc sur une durée minimale de 13 mois. Pour joindre l’école membre de l’AECQ la plus près de chez vous, consultez la liste de nos membres possédant un permis d’enseignement automobile sous la rubrique: